Prevention and control of AMR in hospitals
What can you do as a healthcare specialist against antibiotic resistance?
Health care workers have a vital role in preserving the power of antimicrobial medicines.
Inappropriate prescribing and dispensing of antibiotics can lead to their misuse and overuse, especially if: medical staff lack up-to-date information, cannot identify the type of infection, yield to patient pressure to prescribe antibiotics, or benefit financially from supplying the medications.
(Source: World Health Organization. Global action plan on antimicrobial resistance. Geneva: WHO; 2015.)
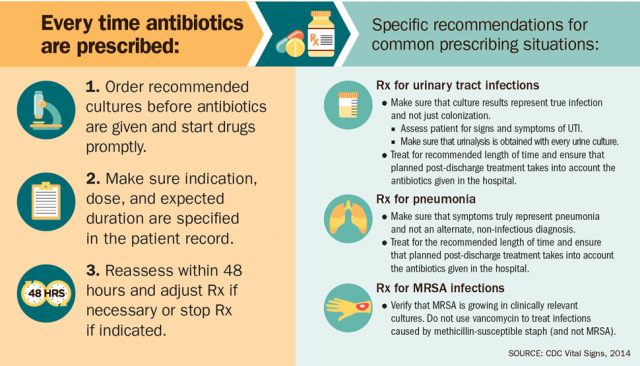
What to do at the hospital ward level
Clinical team
- Limiting antibiotic use – use antibiotics only when required and inform patients about it
- Use antibiotics only when required, follow professional guidelines and protocols
- How to inform patients about the risks of antibiotic resistance and appropriate use of antibiotics and alternative treatments for viral infections such as common colds and flu: https://antibiotic.ecdc.europa.eu/en/healthcare-workers/materials-primary-care-prescribers
- Use antibiotics only when required, follow professional guidelines and protocols
- Appropriate antibiotic treatment as soon as possible
- The importance of appropriate therapy starting on time: https://ccforum.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13054-020-2742-9
- Correct determination of the duration of antibiotic therapy
- How to determine the duration of antibiotic therapy: https://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/22/applications/ABWG_optimal_duration_AB.pdf
Laboratory team
- Provide the clinician as soon as possible with information on which to base a therapeutic decision
- help clinicians to select the most appropriate antibiotics or antibiotic combinations for their patients
- upcoming breakthrough solution: determine the most common antibiotic resistance types with the rapid diagnostic device, the AMRDetecTool
- Pay attention to the drug-resistant infections – report antibiotic-resistant infections to surveillance teams
What to do at the hospital level
Surveillance/epidemiological team (multidisciplinary team)

Set up a team to establish a surveillance program:
– collecting data on AMR
– data analysis and interpretation
– generating local statistics based on results to develop empirical treatment recommendations and AMR control strategies
Accurate surveillance information is essential for antimicrobial stewardship.
Antimicrobial stewardship program
Antimicrobial stewardship program in hospitals is encouraging optimal use of antimicrobials.
The goals of antimicrobial stewardship are to help practitioners pick the right drug at the right dose and duration of therapy while preventing misuse and minimizing the development of resistance.
This review describes all of the important information about antimicrobial stewardship: why, what, who, how, when, and where:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3203003/
Core Elements of Hospital Antibiotic Stewardship Programs:
https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/core-elements/hospital.html
National and international surveillance
Surveillance teams are responsible for reporting the collected data to the central level – the national coordinating centre.
Surveillance data can contribute to the international monitoring program.
Multiple national and international monitoring programs for drug-resistant infections: EARS – Net
https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/about-us/partnerships-and-networks/disease-and-laboratory-networks/ears-net
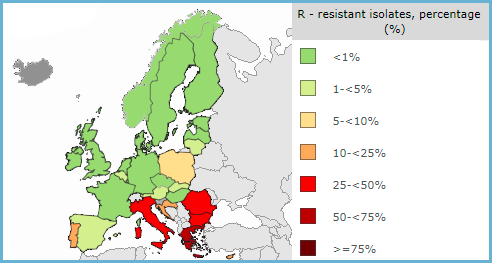
(Prevalence of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae in 2019)
EARS-Net performs surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibility of seven bacterial pathogens commonly causing infections in humans:
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Acinetobacter species
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Enterococcus faecium

Copyright 2020 – AMRDETECTOOL